


(Last Updated: 01/07/2020)
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Hedging: | A risk management strategy to decrease the risk of investment losses by taking a position in a another asset. |
| Speculation: | Buying an asset expecting the price to increase. |
| Arbitrage: | The buying and selling or two financial assets simultaneously to capitalise on the difference in their prices. |
Step 1: Collect and assess the financial data of the client.
Step 2: Determine the goals and objectives of the client.
Step 3: Analyse the client’s needs and identify any financial problems in strategy formulation.
Step 4: Structuring the Statement of Advice (SOA).
Step 5: Recommendations and implementations.
Step 6: Review and monitor.

Issued By: Government
Market: Money
Term: Medium to Long (>1 Year)
Type: Discount Security
Liquidity: High
Risk: Low
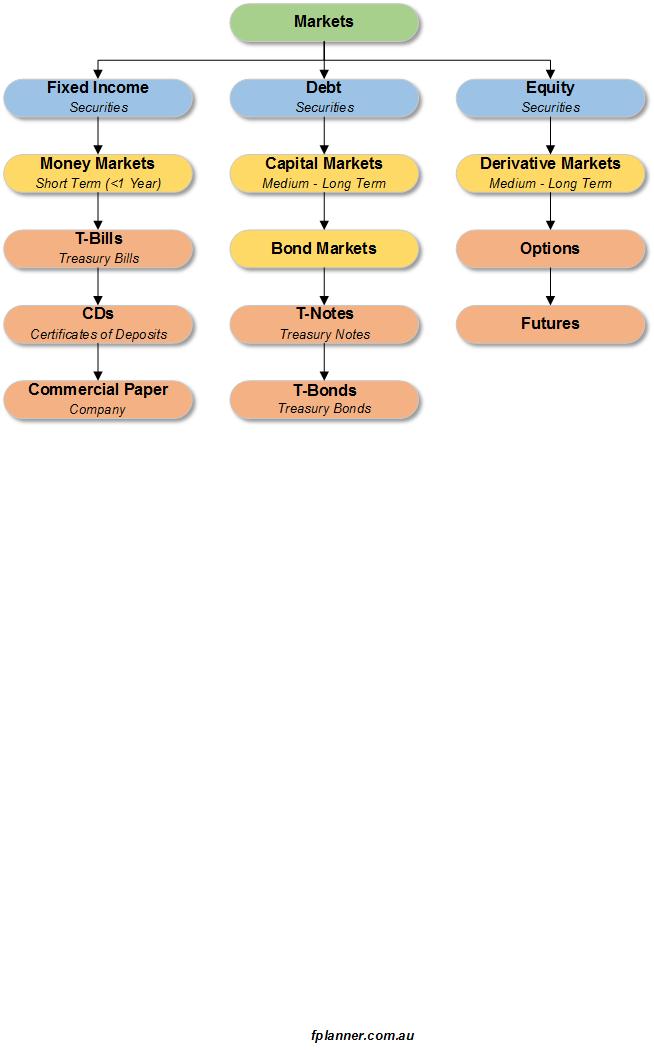
Securities:
>>>
>>>